ADVERTISEMENTS:
After reading this article you will learn about the rock and mineral composition of the earth’s crust.
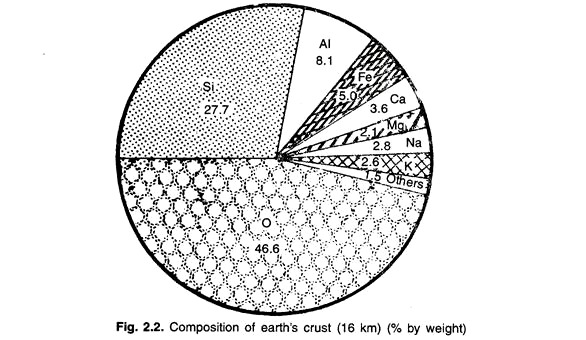
Rock is composed of elements, which in turn are made up of atoms. Out of 106 elements known, 8 are sufficiently abundant as to constitute about 99 per cent by weight of the earth’s crust (up to 16 km) (Table 2.2, Fig. 2.2). The elements are geochemically distributed into five main groups based on their bonding characters.
(i) Lithophile Elements:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Which ionize readily or form stable oxyanions, viz. O, Si, Ti, Fe, Mn, Al, H, Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, B, Ga, Ge, Sn, Sc, Y, F, CI, Br, I, C, HF, Th, P, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, W, U, Zr, (Mo), (Cu), (Zn), (Pb), (Tl), (As), (Sb), (Bi), (S), (Se), (Te), (Ni), (Co), and rare earths.
(ii) Chalcophile Element:
Which tend to form covalent bonds with sulphide, viz. S, Se, Ie, (Fe), Ni, Co, Cu, Zn, Pb, Mo, Ag, Sb, (Sn), Cd, In, Tl, Pb, As, Bi, Re, (Mn), (Ga) and (Ge).
(iii) Siderophile Elements:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Which readily form metallic bonds, viz. Fe, Ni, Co, Ru, Rh, Pd, Ir, Os and Au.
(iv) Atmosphile Elements:
Which tend to remain in atmospheric gases, viz., N, (O), He, Ne, Ar, Kr, and Xe.
(v) Biophile Elements:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Which tend to be associated with living organisms, viz. C, H, O, N, P, S, CI, I, B, Ca, Mg, K, Na, Mn, Fe, Zn, Cu, Ag, Mo, Co, Ni, Au, Be, Cd, Se, Tl, Sn, Pb, As and V.
The elements shown in parentheses fall in the additional group or groups because bonding of the element changes with various factors like temperature, pressure, oxidation or reduction state or other biochemical processes. The earth’s crust consists mainly of the lithophile elements that are commonly found in silicates and soils.
The materials of the earth’s crust fall into two main categories:
(a) Rocks and
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(b) Minerals.