ADVERTISEMENTS:
After reading this article you will learn about the meaning and moisture levels of soil consistency.
Meaning of Soil Consistency:
Soil consistency is also an important physical and dynamic property which varies with the variation of soil moisture and applied stress. So for the discussion of soil consistency, knowledge of soil water like mode of attraction of water by soil materials etc. is a prerequisite. So soil consistency is being discussed as a separate chapter after giving some idea about soil water.
Consistency is the behaviour of soil under stress. This stress is commonly evidenced by feeling the soil, manipulating it by hand, or by tillage operation. Soil consistency is considered a combination of soil properties dependent upon the forces of attraction between soil particles as influenced by soil moisture.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
“Soil consistency is defined as the manifestations of the physical forces of cohesion and adhesion acting within the soil at various moisture constants. These manifestations include the behaviour towards gravity, pressure, thrust and pull; the tendency of the soil mass to adhere to foreign bodies or substances; the sensations which are evidenced as feel by the fingers of the observer”.
Cohesion refers to the attraction of substances of like characteristics such as that of one water molecule for another. Adhesion is the attraction of unlike materials i.e., attraction of water molecule for the soil particle.
Soil consistency depends on the texture, nature and amount of inorganic and organic colloids, structure and moisture content etc. With decreasing moisture content, the soils lose their stickiness and plasticity and become friable and soft and finally when dry become hard and coherent.
Moisture Levels of Soil Consistency:
Soil consistency is described on the basis of three moisture levels wet, moist and dry. In addition, soil consistency is also expressed based on the degree of cementation.
1. Wet Soils:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
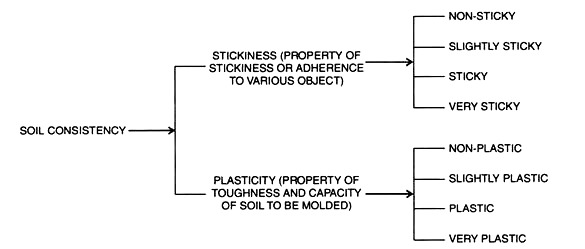
a. Sticky:
After pressure, soil material adheres to both thumb and finger and tends to stretch somewhat and pull apart rather than pulling.
b. Plasticity:
Plasticity is the ability to change shape continuously under the influence of an applied stress and retain the impressed shape on removal of the stress.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
c. Non-Sticky:
After release of pressure, practically no soil material adheres to thumb or finger.
d. Slightly Sticky:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Slight adherence to thumb and finger.
e. Sticky:
After pressure, soil material adheres to both thumb and finger and tends to stretch somewhat and pull apart.
f. Very Sticky:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
After pressure, soil material adheres strongly to fingers.
g. Non-Plastic:
No “wire” is formable when the soil material is rolled between thumb and fore finger.
h. Slightly Plastic:
“Wire” is formable, but soil mass is easily deformable.
i. Plastic:
“Wire” is formable, moderate pressure is required for deformation.
j. Very Plastic:
“Wire” is formable, sufficient pressure is required for deformation.
2. Moist Soils:
Moist consistency when soil is moist is determined at a moisture content approximately midway between air-dry and field capacity. The consistency of moist soils is most important since it best describes the condition of soils when they are tilled in the filed. Consistency of a moist soil is described starting from the least coherence material to the strongly adherence material.
3. Dry Soils:
The consistency of soil material when dry is characterized by rigidity, brittleness, maximum resistance to pressure, tendency to crush to a powder and inability of crushed material to cohere again when pressed together.
Cementation:
Some soil horizons exhibit cementation quite independent of soil moisture level. The cementing agents are generally oxides of iron and aluminium, calcium carbonate and silica.
Another important character of soil consistency is the scouring point. This point represents that moisture content at which the soil no longer sticks to a foreign object. With highly plastic soils, the scouring point lies slightly below the liquid limit, with slightly plastic soils it occurs above the liquid limit.